| Click here for Specification
General Principles
Structured wiring allows for the flexible use of a buildings cabling network to run computers and telephones. The system is totally flexible, in so much as the user can move apparatus from one office to another without
resorting to any engineering work This is achieved by point to point wiring and flooding the building with RJ45 sockets (intermediate
patch enclosures can also be installed). The whole system is built in accordance with the Category 5 wiring specification
and only approved equipment may be used. Cat 5
cable looks the same as telephone cable but is made to a higher specification. All terminations on a structured cabling
system are made without removing any twists from the cable and each socket is tested. The test results are presented to the
customer and this forms the guarantee. As some guarantees last for 15 years or more - do not tamper with these wiring
systems and under no circumstances repair a broken cable - it must be renewed completely.
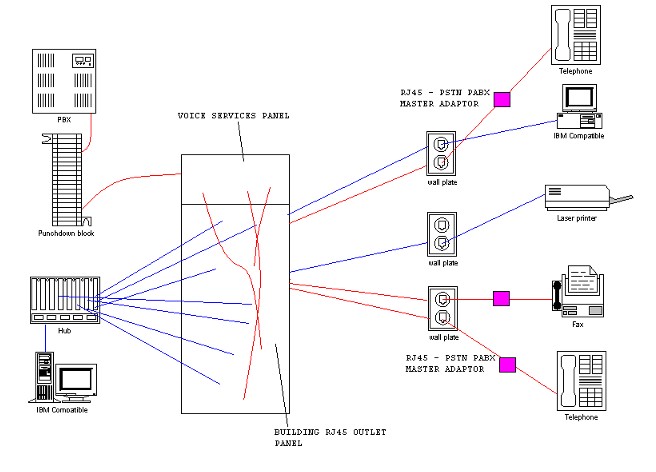
Overview of Installation
The telephone system is wired to a central patch panel consisting of RJ45 sockets. Extensions are cross connected from the
telephone system patch panel to the building wiring patch panel using
RJ45 plug ended patch cables. These patch cables are straight connected and must not be confused with twisted
cables (that look similar) that are used on ISDN equipment. Patch cables may differ
in colour
and this is for identification purposes only, as they electrically the same.
At the end of the building cable is a RJ45 socket. Telephones
may have to be connected to the RJ45 socket and this may be achieved by the use of:-
Adapters come in three types:-
-
PSTN Master, used for Exchange lines when connected to POT phones and Fax
machines etc (has a ring circuit capacitor, test resistor and high voltage protector).
-
PBX Master, as above but without resistor and high voltage protector.
-
Secondary/slave adapter, used for supersets or apparatus that does not require a ring circuit capacitor.
All sockets and patch panels should be labelled and records should be kept of all
connections.
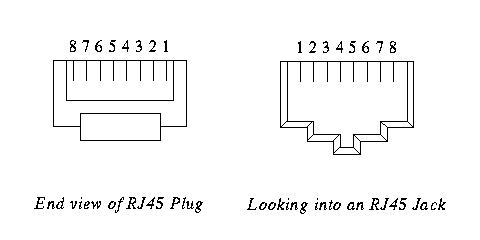
RJ45 Wiring
Pinouts for RJ45 jacks (Serial and 10Base-T)
Connecting Telephone Apparatus
To ensure that telephones will work when connected to a structured cabling system the wiring must be correctly terminated at the first patch panel. Extension wiring should be connected as follows:
|
Telephone system
|
RJ45 socket on Patch panel
|
|
| A |
4 |
|
| B |
5 |
|
| Earth |
1 |
|
Only straight patch leads should be used to cross connect between patch panels (see diagram above).
 BT adaptors BT adaptors
For a UK telephone to be connected to an RJ45 socket a converter adaptor must be used. There are two sorts - one cord
ended (as shown) and the other that plugs directly into the socket.
The wiring of the adaptor is shown below. There are three sorts of adaptors: PSTN, PABX Master and Secondary. Ensure that you purchase the correct version for your needs.
The PBX master is used when POT phones are connected and the Secondary type used for System Featurephones.
Be careful to ensure that if you use earth recall that the adaptors have a connection to pin 4 on the BT socket side of the
adaptor.
Adaptor wiring
RJ45
Socket |
RJ45 Plug
|
BT Plug
|
|
| 1 |
1 |
4 |
Recall - if wired |
| 2 |
2 |
- |
Ring - Not connected |
| 3 |
3 |
6 |
|
| 4 |
4 |
2 |
B leg |
| 5 |
5 |
5 |
A leg |
| 6 |
6 |
1 |
|
| 7 |
7 |
- |
|
| 8 |
8 |
- |
|
Common problems
Analogue telephone (POT) does not ring or only rings once:
- Earth connected wrongly in Patch panel wiring.
- Secondary adapter used (structured wiring system).
ISDN adapter does not work:
|


 BT adaptors
BT adaptors